Treat Lung Cancer with EAnnatto Tocotrienols
Many conservative treatments of cancer like chemotherapy, surgery, and radiation have failed to eliminate lung cancer completely. In a report by World Health Organisation (WHO), dated 12 September 2018, it was observed that approximately1.8 million deaths happened due to Lung cancer that year which is the largest number as compared to other cancers! Henceforth it won’t be wrong to say that lung cancer is the deadliest cancer. Moreover lung cancer has been observed to be the 2nd most common cancer in both men and women and about 13% of all new cancers are lung cancers and trust me, a share of 13% amongst all cancers is a huge share. Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer death among both men and women. Each year, more people die of lung cancer than of colon, breast, and prostate combined. Overall the chance that man will develop lung cancer in his lifetime is about 1 in 15 while for a woman; the risk is 1 in 17. These numbers include both smokers and non – smokers.
In the pursuit to fight cancer, researchers have discovered Tocotrienol which is supposed to demonstrate anti-cancer activities. A number of studies have been conducted over Annatto based Tocotrienol (DeltaGold – Eannatto). Several studies have been conducted on Tocotrienol for its effects against lung cancer like ‘Delta-Tocotrienol inhibits non-small lung cancer cell invasion via the inhibition of NF-kb, uPA activator, and MMP-9’, where it was observed that Delta-Tocotrienol attenuated tumor invasion and metastasis by the repression of MMP-9/uPA via downregulation of Notch-1 and NF-kB pathways and upregulation of miR-451, another study, ‘Tocotrienol – rich mixture inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis vie down – regulation of the Notch – 1/NF – kB pathway in NSCLC cells’ in which the anticancer property, “inhibition of cell proliferation” of Tocotrienols was observed.
Study 1 – Delta-Tocotrienol hinder non-small lung cancer cell attack via the inhibition of NF-kb, uPA activator, and MMP-9
Non – small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) accounts for 85% of all lung cancer cell and can be classified into 3 sub – type’s squamous cell carcinoma, large cell carcinoma, and adrenocarcinoma. The initial stage of NSCLC has a 5 year survival rate of 55% but this rate reduces to less than 4% for cases diagnosed with remote metastasis. Matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP – 9) is an enzyme with 21 subtypes in humans which regulates cell migration, angiogenesis, adhesion, aggregation, and immune response in cancer. In this process, MMP – 9 is mainly accountable for humiliating collagen type 4 and elastin in basal membranes, facilitating lung cancer metastasis. High levels of MMP – 9 have also been reported in the serum of lung carcinoma patients. Thus, the modulation of MMP – 9 protein expressions and their activities would be excellent therapeutic targets for the inhibition of assault and metastasis processes in NSCLC.
Urokinase – type plasminogen activator (uPA), a serine proteinase, binds to the urokinase – type plasminogen activator receptor (uPAR) and transforms inactive plasmin and other protease, including MMP – 9, into their active forms. Regulating uPA is one of the major approaches that can directly modulate MMP – 9 activities in cancer. Increased expression of the uPA system has been reported in NSCLC tissue as compared to common lung tissue. It has been observed that nuclear factor – kB (NF – kB) a transcription factor (TF) involved in cancer instigation and progression directly binds with the uPA promoter in vitro. The same study showed that the inhibition of Nf – kB activities decreased cell attack and uPA synthesis in NSCLC cells.
Previous studies showed that Delta – Tocotrienol (Eannatto – DetaGold) subdued NF – kB signaling pathways via the down regulation of Notch – 1, thereby decreasing the proliferation and metastatic/invasion potential, while inducing apoptosis of NSCLC cells in a concentration and time – dependent manner. This study investigated the anti – metastatic effect of Delta – Tocotrienol (Eannatto – DeltaGold) on NSCLC cells with the hypothesis that MMP – 9 – dependent invasion and metastasis of NSCLC cells were inhibited by the suppression of Notch – 1 – mediated NF – kB and uPA pathways and induction of miR – 451.
Results
- It was showed that a concentration – dependent reduction in cell proliferation in cancer cells with the addition of Delta – Tocotrienol (Eannatto – DeltaGold).
- Inhibition of cell invasion and migration by Delta – Tocotrienol (Eannatto – DeltaGold) was observed.
- Inhibition of cell aggregation at 30 μM of Delta – Tocotrienol (Eannatto – DeltaGold) in cancer cells and adhesion capabilities by DeltaGold were demonstrated.
- DeltaGold was observed to suppress expression of MMP – 9.
- Delta – Tocotrienol (Eannatto – DeltaGold) was observed to increase the expression of miR – 451. miR – 451 plays a key role on different aspects of carcinogenesis in lung cancer including tumor growth, invasion, radio resistance, and chemoresistance.
- Delta – Tocotrienol (Eannatto – DeltaGold) was also observed to inhibit expression uPA and Notch – 1 pathway proteins.
- Inhibition of NF – kB DNA – binding activity was demonstrated by Delta – Tocotrienol (Eannatto – DeltaGold).
Study 2 –Tocotrienol – rich blend reduce cell proliferation and persuade apoptosis via down – regulation of the Notch – 1/NF – kB pathway in NSCLC cells
It has been observed that aberrant Notch – 1 expression have been reported in lung cancer patients and could potentially be a beneficial molecular/therapeutic target against NSCLC. Tocotrienols, isomers of Vitamin E, have been shown to exhibit antitumor activity via inhibition of different signaling pathways in tumor cells. This study was conducted on commercially available Tocotrienols (a mixture of isomers) on the Noth – 1 pathway in NSCLC, adenocarcinoma (A549) and squamous cell lung cancer (H520) cell lines. A dose – dependent decline in all growth, cell migration, and tumor invasiveness was observed in both cancer cell lines with the addition of Tocotrienols. A significant induction of apoptosis was also observed using Annexin V stain in flow cytometry analysis. Since Tocotrienols significantly affected proliferation, apoptosis, migration, and invasiveness, reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction and Western blot analysis were used to explore the molecular mechanisms responsible for the regulations by testing the expression of Notch – 1 and its downstream genes. A dose – dependent decrease in expression of proteins was observed in Notch – 1, Hes – 1, Survivin, and Bcl – XL. In addition, a mechanism was founded linking the NF – kB pathway and Notch – 1 down regulation from Tocotrienols inhibits cell growth, migration, and tumor cell invasiveness via down regulation of Notch – 1 and NF – kB while inducing apoptosis. Hence, these commercially available Tocotrienol – rich mixture could potentially be an effective supplementation for lung cancer prevention.
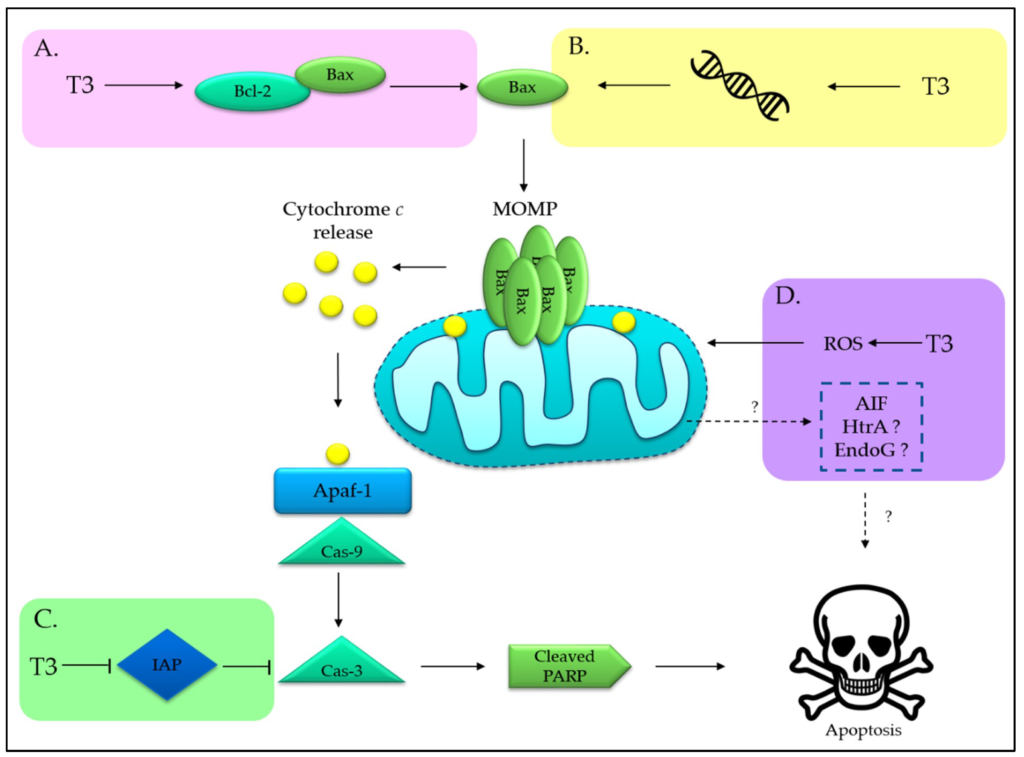
Two different NSCLC cell lines, representing squamous cell carcinoma (H520) adenocarcinoma (A549) were cultured in Rosewell Park Memorial Institute (RPMI), medium (Mediatech, Manassas, VA, USA) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and 1% penicillin and streptomycin in 5% CO2 and 37 degree Celsius. Tocotrienol – rich capsules provided by Carotino (Kula Lumpur, Malaysia), containing 21.3% Tocopherols and 78.7% Tocotrienols, were used in this study. The Tocotrienols in the capsules contained 26.7% Alpha – Tocotrienol, 3.3% Beta – Tocotrienol,, 38.1% Gamma – Tocotrienol and 10.6 Delta – Tocotrienol isomers, whereas the remainder 21,3% composed of Alpha – Tocopherol isomer. The media containing dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) (vehicle control) or different concentrations of TRMC diluted from a 100 mg/mL stock solution were used as experimental treatment media for cell culture. The final concentrations of treatment media is expressed as the amount of TRMC (mg) in 1 mL of RPMI media (mg/mL).
Results
- Anti – proliferative effects of TRMC on NSCLC cell lines were analyzed using MTS assay where anti – proliferative effects of the Tocotrienol mixture were demonstrated.
- Cell death detection histone/deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) Kit from Roche (Palo Alto, CA, USA) was used to detect apoptosis in NSCLC cells. A549 and H520 cells were seeded into 6 – well plates at the density of 1×105and 1×106 cells, respectively and after an overnight incubation, cells were treated with control medium or treatment medium 9different concentrations of TRMC)for 72 hour. Further proceedings showed that apoptosis or programmed cell death was induced in the cancer cells when acted upon by the mixture of Tocotrienols.
- Tocotrienols were observed to induce apoptosis in lung cancer in cell lines.
- Inhibition of cell assault and migration by Tocotrienols was observed. The effect of TRMC on tumor cell invasion and migration was evaluated using Matrigel invasion and wound – healing assays. TRMC concentrations (0.4 – 0.12 mg/mL) resulted in a significantly decreased saturation of lung cancer cells through the Matrigel – coated membrane as compared to the control cells, confirming that TRMC compact the invasion capacity of lung cancer cells. For further confirmation of anti – migratory effects of TRMC, the wound – healing assay was performed. The results of the wound – healing assay exposed that there was decline in cell migration from custom – made wounds with 0.8 mg/mL of TRMC after 30 hours of incubation. In contrast, there was a significant wound healing in the control cells without TRMC, under the same incubation conditions.
- Down regulation of the Notch – 1 and its target gene expressions by Tocotrienols was observed.
- Inhibition of NF – kB DNA binding activity with Tocotrienols was observed.
Summary
Why Tocotrienol?
- Antioxidants, especially Tocotrienol was observed to demonstrate anti-cancer activity against lung cancer cells.
- Angiogenesis which is the process of formation of blood vessels in cancer cells like in your brain cancer. Tocotrienol promotes cancer cell death to a very great extent and good results of anti-angiogenesis property of Tocotrienols have been observed against lung cancer cells in the study.
- Apoptosis or programmed cell death is the process of elimination and death of cancer cells. All isoforms of Tocotrienols have been observed to induce apoptosis in lung cancer cells through the activation of caspase-8 and mitochondrial cyt.c release. Tocotrienol was also reported to tempt apoptosis in human lung adenocarcinoma that harbors Ras mutation.
- Cell Proliferation is the process by which cancer cells copy their DNA and divide into two cancer cells during mitosis and rapidly multiply into more cancer cells. It was observed that Delta-Tocotrienol reticent lung cancer cell proliferation, induce cancer cell death and prevented cell cancer invasion.
- Chemoprevention and anti-cancer activity against lung cancer have been observed in Tocotrienols. Delta-Tocotrienol was observed to exert anti-cancer activity in lung cancer by elevating microRNA, miR-34a, that led to the downregulation of Notch-1 and its downstream targets such as Bcl-2, cyclin D1, and survivin. Moreover, it was also observed that a redox-silent analogue of Alpha-Tocotrienol, 6-O-carboxypropyl-alpha-tocotrienol was found to possess higher anti-cancer potential than Tocotrienol in A549 lung cancer cells.
- Hypoxia adaptation of lung cancer cells was observed to be suppressed by Tocotrienol through the inhibition of Src-induced Akt activation and decreased HIF-2 alpha.
- Cancer stem cell death has been observed by the action of Tocotrienols especially Delta – Tocotrienols (DeltaGold – Eannatto). Even after chemotherapies, radiation and surgeries, there are stem cells of those cancerous tissues left revolving in your body which can lead to your cancer coming back. Henceforth, their death is very necessary and Tocotrienols have been observed to kill cancer stem cells.
Dosage
- Under the study, 900 mg/day of Tocotrienols were used to treat lung cancer cells and no adverse effects were observed and the death of breast cancer cells was witnessed.
- Substances that complement Tocotrienol for cancer include Vitamins C, D, Selenium, B complex.
Why Tocotrienol and Not Tocopherol?
- Tocopherol, the enemy of Tocotrienol: Tocopherol has been observed to ease lung cancer inhibition, inhibits absorption, reduces adipose storage, and compromises cholesterol and triglyceride reduction. Tocopherol hinders the functioning of Tocotrienol and even when they are consumed simultaneously, Tocopherol obstructs all the functions of Tocotrienol.
- Tocopherol, the antagonist in liver cancer treatment:It has been observed that Tocopherol not only interfered with the functioning of Tocotrienol but also showed unsafe effects during the treatment.
- Tocotrienol, the protector of State: Tocotrienol has more mobility than Tocopherol due to its small structure so it can cover a larger area targeting more number of lung cancer cells.
- Small structure and less molecular weight: The higher anti-oxidant activity of Tocotrienols is due to their small structure and less molecular weight which help in their integration of the cell, unlike Tocopherols.
References
- Tocotrienols: Latest Cancer Research in Vitamin E by Barrie Tan, Ph.D., and Anne M.Trias, MS.
- Tocotrienols: The Promising Analogues of Vitamin Efor Cancer Therapeutics
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2018.02.017
- Delta-tocotrienol inhibits non-small-cell lung cancer cell invasion via the inhibition of NF-κB, uPA activator, and MMP-9.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30100736
- Tocotrienol – rich mixture inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis via down – regulation of the Notch – 1/NF – kB pathway in NSCLC cells.
For more details visit our website: https://www.eannatto.ca
